What is the most common crime in Argentina
Crime is a major issue affecting many countries around the world, and Argentina is no exception. From petty theft to violent crimes, understanding the most prevalent offenses can aid in developing effective strategies to address them. In this article, we will delve into the statistics and explore the complexities of Argentina's crime landscape, identifying the most common crime that has plagued the nation for years.
What is the Most Common Crime in Argentina?
Defining the single "most common" crime in Argentina is challenging due to variations in data collection, reporting practices, and the complexities of classifying criminal activities. Different sources may emphasize different types of crime depending on their methodologies. However, based on available data from Argentinan governmental sources and reputable news outlets, theft, in its various forms, consistently emerges as one of the most prevalent crimes across the country.
Types of Theft in Argentina
Theft in Argentina encompasses a wide spectrum of offenses. This includes street crime such as pickpocketing and bag snatching, particularly in crowded urban areas. Residential burglaries are also common, targeting homes and apartments, often for electronics, jewelry, and cash. Vehicle theft, including both carjacking and theft of unattended vehicles, is another significant problem. The prevalence of each type varies regionally, with larger cities experiencing higher rates of street crime and metropolitan areas facing more car theft.
The Role of Socioeconomic Factors
Argentina's complex socioeconomic landscape plays a significant role in crime rates. High levels of poverty and inequality create an environment where some individuals resort to crime for survival. Lack of economic opportunity, particularly among young people, can contribute to involvement in criminal activities. Furthermore, inadequate social safety nets and limited access to education and employment can exacerbate these issues, fostering a cycle of poverty and crime.
Data Collection and Reporting Challenges
Accurate crime statistics in Argentina can be difficult to obtain due to several factors. Underreporting of crimes is a significant issue, with many victims choosing not to report incidents to authorities due to fear, distrust, or a lack of faith in the justice system. Inconsistencies in data collection methods across different jurisdictions can also lead to discrepancies in reported crime rates. Therefore, available statistics should be interpreted cautiously, recognizing the limitations inherent in the data collection process.
The Impact on Tourism
High crime rates, especially petty theft, can significantly impact Argentina's tourism sector. Tourist areas are often targeted by criminals, leading to negative experiences for visitors and potentially deterring future tourism. This impacts the national economy and highlights the need for effective crime prevention strategies and improved security measures in popular tourist destinations.
Law Enforcement and Crime Prevention Strategies
The Argentinian government has implemented various strategies to combat crime, including increased police presence in high-crime areas, improved community policing initiatives, and efforts to enhance investigative capabilities. However, challenges remain, including resource limitations and the need for comprehensive crime prevention programs that address the underlying socioeconomic factors contributing to criminal activity. The effectiveness of these strategies varies across different regions and crime types.
| Crime Type | Description | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Theft | Pickpocketing, bag snatching, burglary, vehicle theft | High |
| Drug Trafficking | Illegal production, distribution, and sale of narcotics | Significant |
| Violent Crime | Assaults, robberies, homicides | Relatively lower than theft, but still a concern |
What is the most common cause of death in Argentina?

The most common cause of death in Argentina is cardiovascular disease. This encompasses a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, stroke, and other related illnesses. While specific statistics fluctuate year to year, cardiovascular disease consistently accounts for the largest portion of mortality in the country.
Cardiovascular Disease Breakdown in Argentina
Cardiovascular disease is a broad term encompassing several life-threatening conditions. Understanding its various components is crucial for effective prevention and treatment strategies in Argentina. The high prevalence is often linked to lifestyle factors and underlying health conditions.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This involves the build-up of plaque in the arteries supplying the heart, leading to reduced blood flow and potentially heart attacks.
- Heart Failure: This occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, leading to shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling.
- Stroke: A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain damage. This can result in long-term disability or death.
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Argentina
Several factors contribute to the high incidence of cardiovascular disease in Argentina. Addressing these risk factors is essential for reducing mortality rates. Lifestyle modifications and improved access to healthcare play a significant role.
- Diet: A diet high in saturated fats, salt, and processed foods increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular physical activity contributes to obesity and other risk factors.
- Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: These conditions increase the risk of cardiovascular events.
- Diabetes: Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for cardiovascular complications.
Healthcare Access and Cardiovascular Disease in Argentina
Access to quality healthcare plays a critical role in preventing and managing cardiovascular disease. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to improving outcomes. Disparities in access to healthcare can exacerbate the problem.
- Early Detection and Prevention Programs: Widespread implementation of programs to screen for risk factors and promote healthy lifestyles is crucial.
- Access to Medications and Treatments: Ensuring affordable access to medications and advanced treatments is essential for managing cardiovascular conditions.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Adequate healthcare infrastructure, including hospitals and trained medical professionals, is necessary to provide effective care.
Socioeconomic Factors and Cardiovascular Mortality in Argentina
Socioeconomic factors are strongly linked to cardiovascular disease prevalence and mortality. Addressing inequalities in access to resources and opportunities is crucial for reducing health disparities.
- Poverty and Access to Healthcare: Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds often have limited access to preventative care and treatment.
- Education and Health Literacy: Higher levels of education and health literacy are associated with healthier lifestyles and better health outcomes.
- Stress and Socioeconomic Instability: Chronic stress associated with poverty and economic instability can negatively impact cardiovascular health.
Government Initiatives and Public Health Campaigns
Argentina's government plays a significant role in addressing cardiovascular disease through public health initiatives and campaigns aimed at raising awareness and promoting preventative measures. These initiatives can significantly impact the overall health of the population.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Campaigns educating the public about risk factors and healthy lifestyle choices are essential.
- Investment in Healthcare Infrastructure: Government investment in healthcare infrastructure improves access to quality care.
- Regulation of Food and Tobacco: Regulations that promote healthy food choices and discourage tobacco use are vital.
What country has the worst crime?

Defining "worst crime" is complex and depends heavily on how crime is measured. There's no single, universally agreed-upon metric. Different countries have varying definitions of crimes, reporting systems, and policing strategies, making direct comparisons challenging. Global crime statistics are often incomplete and unreliable, further complicating any attempt to declare one country definitively as having "the worst crime." Some studies focus on homicide rates, while others prioritize property crime or violent crime. This leads to different rankings depending on the criteria used. Therefore, any answer would be inherently subjective and dependent on the chosen metric.
Challenges in Measuring Global Crime Rates
Accurately measuring crime rates across countries faces significant hurdles. Underreporting is a pervasive issue, particularly in countries with weak law enforcement or where victims fear reprisal. Different methodologies used by nations make comparing data directly problematic. For instance, some countries might classify certain acts as misdemeanors while others consider them felonies. Moreover, variations in police effectiveness and resources can dramatically impact reported crime statistics.
- Data Collection Discrepancies: Inconsistencies in data collection methods (e.g., survey methodologies, police reporting practices) prevent fair comparisons.
- Underreporting of Crime: Many crimes, especially those involving vulnerable populations, go unreported due to fear, mistrust of authorities, or lack of faith in the justice system.
- Definition of Crime: Different legal systems define crimes differently, affecting the overall crime statistics reported.
Homicide Rates as an Indicator
While not a complete picture, homicide rates are often used as a key indicator of violent crime. Countries with high homicide rates frequently face significant challenges related to organized crime, gang violence, and societal instability. However, focusing solely on homicide rates can mask other forms of criminal activity, like property crime or corruption, that might also significantly impact a nation's well-being.
- High Homicide Rates: Countries with high murder rates often grapple with underlying issues like poverty, inequality, and weak governance.
- Gang Violence and Organized Crime: These factors frequently contribute to high homicide rates.
- Data Limitations: Even homicide data can be unreliable due to underreporting and inconsistent recording practices across countries.
The Role of Poverty and Inequality
Studies consistently show a strong correlation between poverty, inequality, and higher crime rates. Countries facing significant economic disparities often experience higher levels of both violent and property crime. A lack of economic opportunity, limited access to education, and inadequate social support systems can all contribute to criminal activity. These factors can create environments where crime becomes a means of survival or a response to social frustration.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, inequality, and lack of opportunity are strongly linked to increased crime.
- Social Disadvantage: Limited access to education, healthcare, and social services often correlates with higher crime rates.
- Lack of Opportunity: The absence of legitimate pathways to economic success can drive individuals towards criminal activity.
Impact of Political Instability and Corruption
Political instability and widespread corruption often create an environment conducive to crime. Weak governance, lack of accountability, and a compromised justice system allow criminal networks to flourish. When institutions are unable or unwilling to enforce the law effectively, crime rates tend to increase significantly. This can include a rise in violent crime, organized crime, and white-collar crime.
- Weak Governance and Corruption: Ineffective law enforcement and corrupt officials contribute to high crime rates.
- Organized Crime and Terrorism: Political instability often creates an opportunity for these groups to thrive.
- Lack of Accountability: When perpetrators are rarely brought to justice, it encourages further criminal activity.
Property Crime vs. Violent Crime
Distinguishing between property crime (theft, burglary) and violent crime (murder, assault) is crucial. Some countries may have high rates of property crime but relatively low rates of violent crime, and vice versa. This distinction significantly affects how a country's "crime problem" is perceived and addressed. Moreover, the economic impact of property crime can be substantial, leading to significant financial losses for individuals and businesses.
- Property Crime: Thefts, burglaries, and other property crimes can significantly impact the economy and individuals.
- Violent Crime: Murder, assault, and other violent crimes have severe societal consequences.
- Comparative Analysis: It's essential to analyze both types of crime for a holistic understanding of a nation's crime situation.
What is the most common crime?
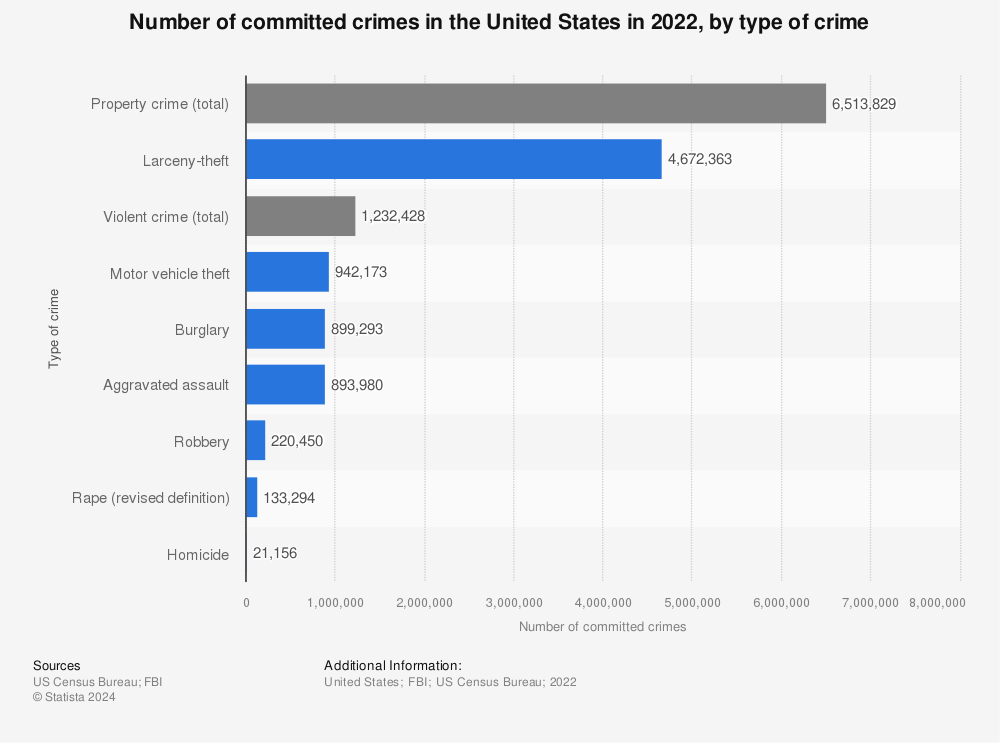
Defining the "most common crime" is challenging because crime statistics vary significantly based on reporting practices, legal definitions, and data collection methods across different jurisdictions. However, theft, in its various forms, is consistently identified as one of the most frequently reported and recorded crimes globally. This broad category encompasses a wide range of offenses, from petty shoplifting to grand larceny, and includes crimes like larceny-theft, motor vehicle theft, and burglary. The sheer volume of these offenses across diverse populations and settings makes theft a strong contender for the title of most common crime.
Defining Theft and its Subcategories
Theft is a broad term encompassing many specific crimes. Accurate comparisons require specifying the type of theft being analyzed. For instance, comparing larceny-theft rates to motor vehicle theft rates doesn’t give a complete picture of overall theft. The variations in legal definitions and reporting procedures across different countries and even within states further complicate any simple ranking. To accurately determine what's "most common," consistent definitions and reporting are crucial.
- Larceny-theft: This includes the unlawful taking, carrying, leading, or riding away of property from the possession or constructive possession of another.
- Burglary: This usually involves unlawful entry into a structure to commit a felony or theft.
- Motor vehicle theft: The theft or attempted theft of a motor vehicle.
Data Collection Challenges and Reporting Bias
Inconsistent data collection significantly impacts the accuracy of crime statistics. Many crimes, particularly those involving less serious forms of theft, go unreported due to various reasons – victims might not believe reporting will lead to recovery of property, they might fear retribution, or they might lack trust in law enforcement. This underreporting skews the data, making it difficult to obtain a truly representative picture of the most frequent crimes.
- Underreporting due to victim reluctance.
- Variations in crime reporting procedures across different jurisdictions.
- Differences in how crimes are classified and categorized.
Geographic Variations in Crime Rates
Crime rates, including theft rates, vary significantly based on geographic location. Factors such as socioeconomic conditions, population density, levels of law enforcement, and cultural norms all influence the prevalence of specific crimes. A crime common in one region might be rare in another, making it difficult to establish a universally applicable "most common" crime.
- Higher crime rates in urban vs. rural areas.
- Influence of socioeconomic factors on crime prevalence.
- Impact of law enforcement strategies on crime statistics.
The Impact of Technology on Crime Statistics
Technology has had a profound impact on both the commission and recording of crimes. The rise of cybercrime, including online theft and fraud, presents a new challenge to accurately capturing crime statistics. Traditional methods of data collection are often ill-equipped to handle the complexities of digital offenses, leading to potential underreporting or misclassification of crimes.
- The increasing prevalence of cybercrime.
- Challenges in tracking and reporting online theft.
- The need for improved data collection methods in the digital age.
Minor Offenses vs. Serious Crimes
When considering the "most common" crime, it is important to distinguish between minor offenses and serious felonies. While petty theft might be more frequently reported than, say, murder, the latter is significantly more impactful. The focus should not solely be on frequency, but also on the societal consequences and severity of various criminal acts. This highlights the limitations of relying solely on raw numbers to define the "most common crime".
- The disparity between frequency and severity of crimes.
- The need to consider the social impact of crime beyond simple counts.
- The importance of understanding the context of crime statistics.
Is crime a problem in Buenos Aires?
Is Crime a Problem in Buenos Aires?
Buenos Aires, like many large global cities, faces a complex issue with crime. The level of crime is a matter of ongoing debate and perception, often varying depending on the specific neighborhood and the type of crime considered. While it's inaccurate to paint the entire city with a single brush, it's undeniable that certain types of crime, particularly petty theft and street crime, are prevalent in some areas. The perception of crime can be significantly amplified by media reporting and anecdotal evidence, making it difficult to establish a fully objective picture. Official crime statistics, while offering some data, often don't fully capture the extent of the problem, especially in underreported areas. This makes judging the severity a nuanced task demanding a careful consideration of multiple factors.
Types of Crime in Buenos Aires
The city experiences a range of criminal activities. Petty theft, including pickpocketing and bag snatching, is a common concern, particularly in crowded tourist areas and on public transportation. More serious crimes, such as robbery and assault, also occur, although their frequency and severity can vary considerably by location. Organized crime, while present, is generally less visible to the average citizen than street crime. The types of crime experienced may also vary significantly depending on the time of day and the area of the city.
- Petty theft: Pickpocketing, bag snatching, and other minor thefts are common, especially in tourist zones.
- Robbery: Armed robberies, though less frequent than petty theft, are a serious concern.
- Assault: Physical assaults can occur, though the frequency varies widely depending on the neighborhood and time of day.
Tourist Safety in Buenos Aires
Tourists should exercise caution and be aware of their surroundings. It's crucial to be vigilant against petty theft, especially in crowded areas. Keeping valuables secure and avoiding displaying expensive jewelry or electronics openly can significantly reduce the risk. Staying in well-lit and populated areas at night is also advisable. While serious crime against tourists is relatively uncommon, it's always best to be prepared and to avoid potentially risky situations. Using official transportation services and being aware of scams can enhance safety.
- Avoid displaying valuables: Keep expensive items hidden and out of sight.
- Use reputable transportation: Stick to official taxis or ride-sharing services.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Stay vigilant and avoid walking alone in poorly lit or isolated areas at night.
Crime Statistics and Reporting
Official crime statistics in Buenos Aires can be challenging to interpret. Data collection methods and reporting practices can vary, making comparisons across time and with other cities difficult. Furthermore, a significant portion of crime, particularly petty theft, may go unreported. This underreporting skews the perception of the true extent of criminal activity. Therefore, relying solely on official statistics to understand the crime situation provides only a partial picture.
- Underreporting: Many crimes, especially minor ones, go unreported to the authorities.
- Data inconsistencies: Variations in data collection methods can lead to inconsistencies in crime statistics.
- Limited data transparency: Access to detailed and reliable crime statistics can be limited.
Neighborhood Variations in Crime Rates
Crime rates in Buenos Aires are not uniform across the city. Certain neighborhoods experience significantly higher crime rates than others. Factors contributing to this variation include socioeconomic factors, levels of policing, and population density. Researching the specific areas you plan to visit is crucial, particularly if you are unfamiliar with the city. Understanding the relative safety of different neighborhoods allows for more informed decision-making.
- Socioeconomic disparities: Poorer neighborhoods often experience higher crime rates.
- Police presence: Areas with a stronger police presence may have lower crime rates.
- Population density: Crowded areas can be more susceptible to certain types of crime.
Safety Precautions and Resources
Visitors and residents alike should take precautions to minimize their risk of becoming victims of crime. This includes being aware of their surroundings, avoiding risky situations, and reporting any crimes to the authorities. Utilizing reliable sources of information about safety and security in Buenos Aires can help visitors make informed decisions and plan their trips accordingly. Local authorities and tourist information centers can provide valuable advice and support.
- Situational awareness: Paying attention to your surroundings is crucial for personal safety.
- Reporting crimes: Report any incidents of crime to the local authorities.
- Seeking reliable information: Consult trustworthy sources for safety and security updates.
What is the most common crime in Argentina?
Defining the single "most common" crime in Argentina is challenging due to variations in data collection, reporting practices, and the complexities of criminal activity. However, based on available data from official sources and journalistic investigations, theft, in its various forms, consistently emerges as a significant concern. This encompasses a broad spectrum of offenses, ranging from petty street crime like pickpocketing and bag snatching, particularly prevalent in tourist areas and crowded urban centers, to more serious incidents involving robbery with violence or threats. The prevalence of theft is largely influenced by socio-economic factors, including high levels of poverty and inequality that contribute to a climate where opportunistic crime flourishes. While specific statistics can fluctuate year to year, reports regularly highlight the considerable impact of theft on both individuals and businesses, making it a pervasive issue across the country. It's also important to distinguish between reported crime and unreported crime; the true scale of theft is likely considerably higher than official figures suggest due to underreporting driven by factors like mistrust in law enforcement, fear of retaliation, or bureaucratic hurdles in filing reports.
Are violent crimes common in Argentina?
While theft is arguably the most frequently occurring crime, violent crime in Argentina, though less common than theft, remains a significant concern. Data on violent crime, including homicide, assault, and armed robbery, varies depending on the source and region. Certain urban areas experience higher rates of violent crime than others. It's important to note that the perception of violent crime can often be disproportionate to its actual frequency, influenced by media reporting and anecdotal evidence. Furthermore, the effectiveness of law enforcement in addressing and reducing violent crime is a subject of ongoing debate and analysis. While official statistics might not always fully reflect the reality on the ground, it's clear that violent crime constitutes a real threat in some parts of Argentina, although it's generally not as widespread as petty theft. Understanding the specific contexts, locations, and risk factors associated with violent crime is crucial for assessing personal safety and taking appropriate precautions.
How does drug trafficking affect crime rates in Argentina?
Drug trafficking significantly influences the overall crime landscape in Argentina, contributing to both violent and non-violent crime. Argentina's geographic location makes it a transit point for drug smuggling, particularly cocaine, impacting both domestic drug markets and international trafficking routes. This illicit trade fuels related crimes, such as money laundering, corruption, and organized crime. The competition between drug cartels often results in increased violence, impacting communities and leading to higher rates of homicide and other serious violent crimes. Furthermore, the demand for drugs creates a market for associated criminal activities, such as drug-related theft and robbery. Addressing the issue of drug trafficking requires a multi-faceted approach, targeting not only the supply chains but also the underlying social and economic factors that contribute to drug use and the associated criminal activity. The complex interplay between drug trafficking and other forms of crime makes it a significant challenge for law enforcement and policymakers.
What measures are being taken to reduce crime in Argentina?
The Argentine government implements various measures to combat crime, although their effectiveness is a subject of ongoing discussion. These measures range from increasing police presence in high-crime areas and strengthening law enforcement capacity to implementing social programs aimed at addressing the root causes of crime, such as poverty and inequality. Community policing initiatives aim to foster better relationships between law enforcement and citizens, improving crime reporting and fostering trust. However, challenges remain, including budgetary constraints, issues of corruption within law enforcement, and the complexity of tackling the deep-rooted socio-economic factors contributing to criminal behavior. Legislative reforms are periodically introduced to adjust sentencing, enhance judicial processes, and address specific criminal offenses. The evaluation of these measures' effectiveness requires comprehensive analysis, considering not only reported crime statistics but also the complexities of the justice system, socio-economic conditions, and public perception of safety.
Deja una respuesta